References:
- Unit Testing.
- White Box Testing.
- Black Box Testing.
- What is WHITE Box Testing? Techniques, Example, Types & Tools.
- Differences Between Black Box Testing and White Box Testing.
Motivation
Recently I am writing unit test for my production codes of ML algorithms, which raises my awareness of the significance of software testing.
I was asked to do the same thing some three years ago; but until now I got my hands dirty and found testing is quite a significant part of the software/algorithm development circle.
So I started to record some of my learnings three years later.
The task
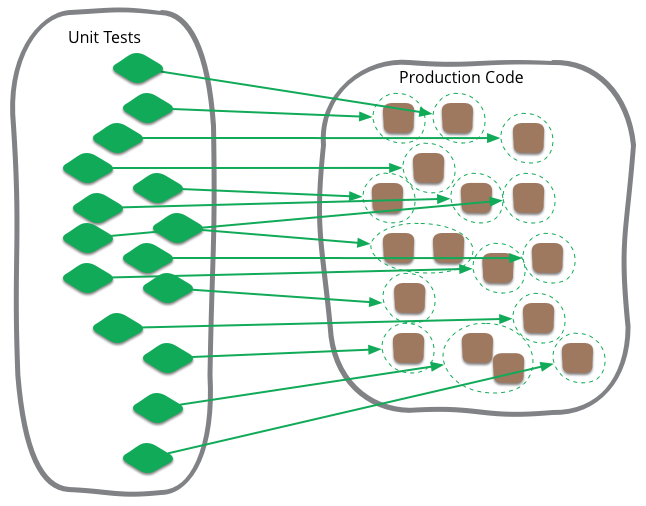
To test the functionality of each class, method, or module.
The tester determines all legal (valid and invalid) AND illegal inputs and verifies the outputs against the expected outcomes.
To verify the flow of inputs and outputs through the application, improving design and usability, strengthening security.
Methods and Concepts
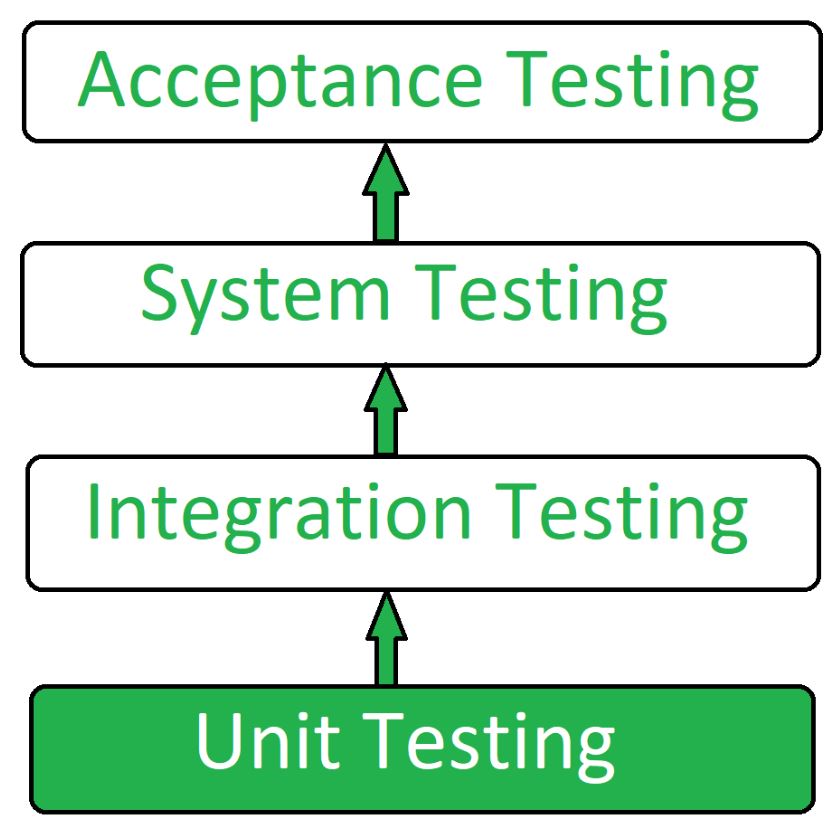
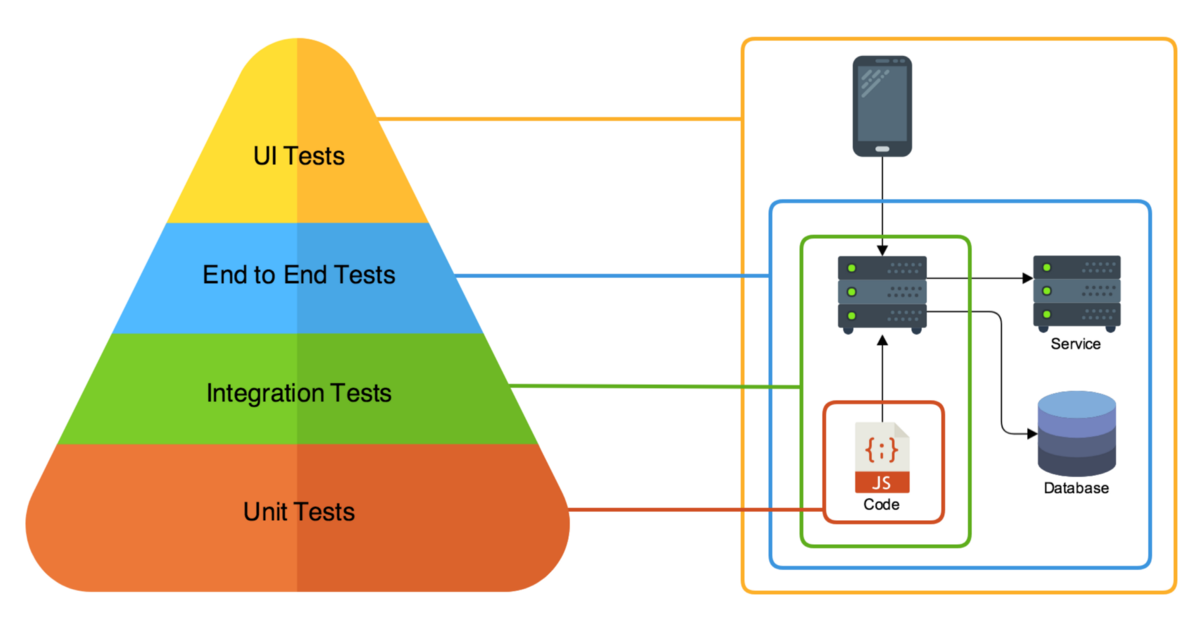
Test scope: within a unit.
Methods
Design the procedure to derive and/or select test cases based on an analysis of the internal structure of a component or system. Two Box Testing methods: White Box Tesing, Black Box Testing
White Box Testing (also structural testing)
- Basics
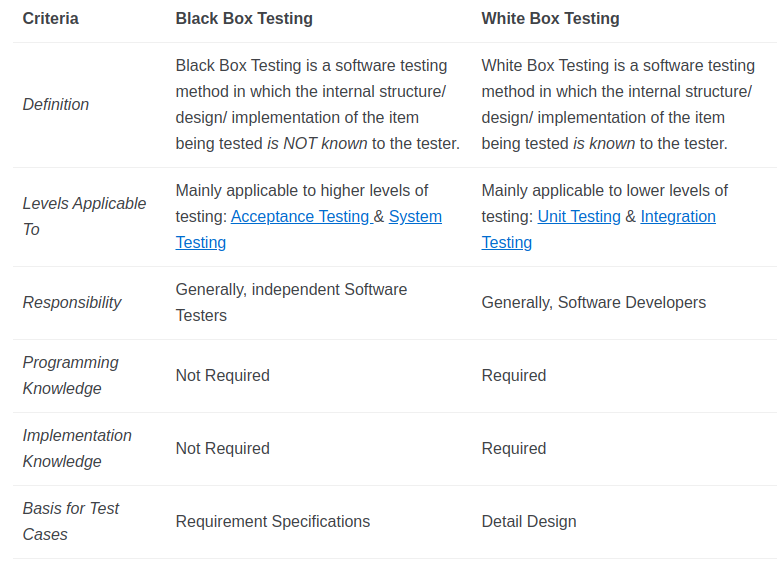
- testing based on an analysis of the internal structure of the component or system.
- the internal structure/design/implementation of the item being tested is known to the tester
- the tester chooses inputs to exercise paths through the code and determines the appropriate outputs
The key being, the software program, in the eyes of the tester, is like a white/transparent box; inside which one clearly sees.
- testing based on an analysis of the internal structure of the component or system.
- Uses
The testing can be done at system, integration and unit levels of software development. One of the basic goals of whitebox testing is to verify a working flow for an application. It involves testing a series of predefined inputs against expected or desired outputs so that when a specific input does not result in the expected output, you have encountered a bug.
White Box Testing method mainly applied to Unit Testing, but it is applicable to the following levels of software testing:
- Unit Testing: For testing paths within a unit.
- Integration Testing: For testing paths between units.
- System Testing: For testing paths between subsystems.
What do you verify in White Box Testing?
White box testing involves the testing of the software code for the following:
- Internal security holes
- Broken or poorly structured paths in the coding processes
- The flow of specific inputs through the code
- Expected output
- The functionality of conditional loops
- Testing of each statement, object, and function on an individual basis
How do you perform White Box Testing?
two basic steps:
- STEP 1) UNDERSTAND THE SOURCE CODE
- Step 2) CREATE TEST CASES AND EXECUTE
- White Box Testing Examples
Consider the following piece of code:
Printme (int a, int b) { ------------ Printme is a function int result = a+ b; If (result> 0) Print ("Positive", result) Else Print ("Negative", result) } ----------- End of the source codeThe goal of WhiteBox testing in software engineering is to verify all the decision branches, loops, statements in the code.
To exercise the statements in the above code, WhiteBox test cases would be
A = 1, B = 1
A = -1, B = -3 - White Box Testing Techniques
A major White box testing technique is Code Coverage analysis. Code Coverage analysis eliminates gaps in a Test Case suite. It identifies areas of a program that are not exercised by a set of test cases. Once gaps are identified, you create test cases to verify untested parts of the code, thereby increasing the quality of the software product.
There are automated tools available to perform Code coverage analysis. Below are a few coverage analysis techniques a box tester can use:
* Statement Coverage:- This technique requires every possible statement in the code to be tested at least once during the testing process of software engineering.
* Branch Coverage - This technique checks every possible path (if-else and other conditional loops) of a software application.
* Apart from above, there are numerous coverage types such as Condition Coverage, Multiple Condition Coverage, Path Coverage, Function Coverage etc. Each technique has its own merits and attempts to test (cover) all parts of software code. Using Statement and Branch coverage you generally attain 80-90% code coverage which is sufficient.
White Box Testing Tools
* Parasoft Jtest
* EclEmma
* NUnit
* PyUnit
* HTMLUnit
* CppUnit
- Advantages
- Testing can be commenced at an earlier stage. One need not wait for the GUI to be available.
- Testing is more thorough, with the possibility of covering most paths
- Code optimization by finding hidden errors.
- White box tests cases can be easily automated.
- Testing is more thorough as all code paths are usually covered.
- Testing can start early in SDLC even if GUI is not available.
- Disadvantages
- Since tests can be very complex, highly skilled resources are required, with a thorough knowledge of programming and implementation.
- Test script maintenance can be a burden if the implementation changes too frequently.
- Since this method of testing is closely tied to the application being tested, tools to cater to every kind of implementation/platform may not be readily available.
- White box testing can be quite complex and expensive.
- White box testing requires professional resources, with a detailed understanding of programming and implementation.
- White box testing is time-consuming, bigger programming applications take the time to test fully.
- Other notes
White box testing can be quite complex. The complexity involved has a lot to do with the application being tested. A small application that performs a single simple operation could be white box tested in few minutes, while larger programming applications take days, weeks and even longer to fully test
Black Box Testing (also known as Behavioral Testing)

- Basics
Testing, either functional or non-functional, without reference to the internal structure of the component or system.
- internal structure/design/implementation of the item being tested is not known to the tester
- can be functional or non-functional, though usually functional.
The key being, the software program, in the eyes of the tester, is like a black box; inside which one cannot see.
This method attempts to find errors in the following categories:
- Incorrect or missing functions
- Interface errors
- Errors in data structures or external database access
- Behavior or performance errors
- Initialization and termination errors
- Uses
Design a procedure to derive and/or select test cases based on an analysis of the specification, either functional or non-functional, of a component or system without reference to its internal structure.
Black Box Testing method is applicable to the following levels of software testing:
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- Acceptance Testing
The higher the level, and hence the bigger and more complex the box, the more black-box testing method comes into use.
- Black Box Testing Techniques
- Equivalence Partitioning: It is a software test design technique that involves dividing input values into valid and invalid partitions and selecting representative values from each partition as test data.
- Boundary Value Analysis: It is a software test design technique that involves the determination of boundaries for input values and selecting values that are at the boundaries and just inside/ outside of the boundaries as test data.
- Cause-Effect Graphing: It is a software test design technique that involves identifying the cases (input conditions) and effects (output conditions), producing a Cause-Effect Graph, and generating test cases accordingly.
- Advantages
- Tests are done from a user’s point of view and will help in exposing discrepancies in the specifications.
- Tester need not know programming languages or how the software has been implemented.
- Tests can be conducted by a body independent from the developers, allowing for an objective perspective and the avoidance of developer-bias.
- Test cases can be designed as soon as the specifications are complete.
- Disadvantages
- Only a small number of possible inputs can be tested and many program paths will be left untested.
- Without clear specifications, which is the situation in many projects, test cases will be difficult to design.
- Tests can be redundant if the software designer/developer has already run a test case.
- Ever wondered why a soothsayer closes the eyes when foretelling events? So is almost the case in Black Box Testing.
Differences Between Black Box Testing and White Box Testing
For a combination of the two testing methods, see Gray Box Testing.